
| |
| Home |
| The Railway |
| Research |
| Staff Records |
| Bibliography |
| Photographs |
| The Society |
| Journal |
| Publications |
| Modelling |
| Contact Us |
| Links |
| The Railway |
|
The original proposals to construct railways to Inverness were made in the mid-1840s. Rival routes were proposed from Perth and Aberdeen . The Perth & Inverness Railway was considered too hilly for the locomotives of the day, but the Great North of Scotland Railway (GNSR) from Aberdeen was authorised. The GNSR struggled to raise capital in the post-railway mania period and eventually started construction as far as Huntly in 1852, opening that line in 1854. The people of Inverness then stepped in and started building their own line from the Inverness end, initially as far as Nairn, the Inverness & Nairn Railway (I&N) was opened on 6th. November 1855 but by then plans were being made to extend this railway to meet the GNSR. After some discussion, the Inverness & Aberdeen Junction Railway (I&AJ) was promoted to build the line from Nairn to Keith where it met the GNSR extension from Huntly. The I&AJ was completed on 18th. August 1858,when it took over the working of the I&N. The people of Inverness were never satisfied with the long journey round via Aberdeen , especially as the GNSR's station was half a mile from that of the line from the south and connections were not always maintained. Thus was born the Inverness and Perth Junction Railway (I&PJR) which ran from Forres via Grantown, Kingussie and Drumochter summit to Dunkeld where it met with end on with the Perth and Dunkeld Railway which had opened in 1856. The I&P was authorised in 1861 and opened just two years later, being worked from the outset by the I&AJR. The two companies amalgamated on 1st. February 1865 to form the Highland Railway. Meanwhile construction northwards from Inverness had already started, with a line to Dingwall (1862), Invergordon (1863), Bonar Bridge (1864), Golspie (1868), Helmsdale (1871) and Wick and Thurso (1874). Westward from Dingwall, the Dingwall & Skye Railway was opened to Strome Ferry in 1870. In the 1890s, two additions were made to the main network. The direct line from Aviemore over Slochd to Inverness was completed in 1898, a year after the Skye line was extended to the present terminus at Kyle of Lochalsh. Several branches were opened from these main lines over the next 40 years, taking the final length of the system to some 242 route miles. Tourist traffic has always been a major source of income for the railways in the Highlands . The Highland Railway developed its own hotels at Inverness , Dornoch and Strathpeffer. It offered combined tours in conjunction with the steamer services of David MacBrayne. Each August it had to contend with the annual migration north for the 'glorious twelfth.' The railway played a major part in the First World War, when the Grand Fleet was stationed at Scapa Flow in the Orkney Islands . Worn down, like many other railways in the country, it became part of the London , Midland and Scottish Railway in 1923. The LMS continued to develop the lines, introducing dining cars and speeding up services. The Second World War again imposed a considerable strain on the lines. On the nationalisation of the railways, the Scottish Region of British Railways took over. Soon the development of road transport made a significant impact on the use of the railway. The closure of branch lines, which had started in the 1930s, continued. The Beeching Plan of 1963 envisaged the closure of all lines north of Inverness , but this was not approved because those lines still provided a lifeline in winter. The old route from Aviemore to Forres and a number of intermediate stations on the main lines, were closed. Otherwise the main system remained intact, as it does today. Currently operated by Abellio on behalf of ScotRail, the lines continue to provide a vital link to locals and bring many tourists to the area. The Highland Railway was well known for its locomotives. Working the steep gradients of the main line, in particular, was always a challenge. Add strong winds and snow and the problems became even worse. The railway introduced the first 4-6-0s to the British Isles, commemorated in the preserved No.103 at the Glasgow Transport Museum . In the 1930s, the LMS Black 5s, locally always called "Hikers", immediately proved their worth. The isolated nature of the country led British Railways to implement complete dieselisation early in the modernisation plan. Today class 158 and 170 diesel multiple units work most of the trains, but you can still retire to bed in a sleeper on the line out of London Euston and wake up to the sound of a Class 67 struggling up Drumochter. |
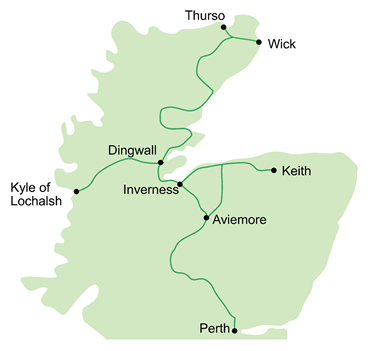 Inverness
was always the centre of the Highland Railway. It was the company's
headquarters and principle station. All trains led to Inverness.
Inverness
was always the centre of the Highland Railway. It was the company's
headquarters and principle station. All trains led to Inverness.